Great Plains
| The Great Plains | |
| Region | |
 View of the Great Plains near Lincoln, Nebraska
|
|
| Countries | United States, Canada |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | |
| Length | 3,200 km (1,988 mi) |
| Width | 800 km (497 mi) |
| Area | 1,300,000 km² (501,933 sq mi) |
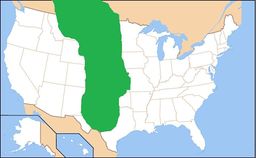 Map of the Great Plains [1]
|
|
| Website: Library of Congress | |
The Great Plains are the broad expanse of prairie, steppe and grassland which lie west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. This area covers parts of the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Texas and Wyoming, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, Manitoba and Saskatchewan. Some geographers include some territory of Mexico in the Plains, but many stop at the Rio Grande. In Canada the term prairie is more common, and the region is known as the Prairie Provinces or simply "the Prairies."
The region is about 500 mi (800 km) east to west and 2,000 mi (3,200 km) north to south. Much of the region was home to American Bison herds until they were hunted to near extinction during the mid/late 1800s. It has an area of approximately 1,300,000 km2 (500,000 sq mi). Current thinking regarding the geographic boundaries of the Great Plains is shown by this map at the Center for Great Plains Studies, University of Nebraska–Lincoln.[1]
Contents |
Geology
The Great Plains are the westernmost portion of the vast North American Interior Plains, which extend east to the Appalachian Plateau. The United States Geological Survey divides the Great Plains in the United States into ten physiographic subdivisions:

- Coteau du Missouri or Missouri Plateau, glaciated – east-central South Dakota, northern and eastern North Dakota and northeastern Montana;
- Coteau du Missouri, unglaciated – western South Dakota, northeastern Wyoming, southwestern North Dakota and southeastern Montana;
- Black Hills – western South Dakota;
- High Plains – eastern New Mexico, northwestern Texas (including the Llano Estacado), western Oklahoma, eastern Colorado, western Kansas, most of Nebraska (including the Sand Hills) and southeastern Wyoming;
- Plains Border – central Kansas and northern Oklahoma (including the Flint, Red and Smoky Hills);
- Colorado Piedmont – eastern Colorado;
- Raton section – northeastern New Mexico;
- Pecos Valley – eastern New Mexico;
- Edwards Plateau – south-central Texas; and
- Central Texas section – central Texas.
The High Plains is used in a related, more general context to describe the elevated regions of the Great Plains, which are primarily west of the 100th meridian in the US.
During the Cretaceous Period (145-65 million years ago), the Great Plains was covered by a shallow inland sea called the Western Interior Seaway. However, during the Late Cretaceous to the Paleocene (65-55 million years ago), the seaway had begun to recede, leaving behind thick marine deposits and a relatively flat terrain where the seaway had once occupied.
Paleontological finds in the area have yielded bones of woolly mammoths, saber toothed tigers and other ancient animals,[2] as well as dozens of other megafauna (large animals over 100 lb (45 kg)) – such as giant sloths, horses, mastodons, and American lion – that dominated the area of the ancient Great Plains for millions of years. The vast majority of these animals went extinct in North America around 13,000 years ago during the end of the Pleistocene.[3]
Climate
In general, the Great Plains have a wide variety of weather throughout the year, with very cold winters and very hot summers. Wind speeds are often high. The prairies support abundant wildlife in undisturbed settings. Humans have converted much of the prairies for agricultural purposes or pastures.
The 100th meridian roughly corresponds with the line that divides the Great Plains into an area that receive 20 in (510 mm) or more of rainfall per year and an area that receives less than 20 in (510 mm). In this context, the High Plains, as well as Southern Alberta, south-western Saskatchewan and Eastern Montana are mainly semi-arid steppe land and are generally characterised by rangeland or marginal farmland. The region (especially the High Plains) is periodically subjected to extended periods of drought; high winds in the region may then generate devastating dust storms. The eastern Great Plains near the eastern boundary falls in the humid continental climate zone in the northern and central areas and the humid subtropical climate zone in the southern areas.
Flora
The Great Plains are part of the floristic North American Prairies Province, which extends from the Rocky Mountains to the Appalachians.
History
Original American contact
The first Americans (Paleo-Indians) who arrived to the Great Plains were successive indigenous cultures who are known to have inhabited the Great Plains for thousands of years, perhaps 10,000 years. Humans entered the North American continent in waves of migration, mostly over Beringia, the Bering Straits land bridge.
Historically, the Great Plains were the range of the bison and of the culture of the Plains Indians, whose tribes included the Blackfoot, Crow, Sioux, Cheyenne, Arapaho, Comanche, and others. Eastern portions of the Great Plains were inhabited by tribes who lived in semipermanent villages of earth lodges, such as the Arikara, Mandan, Pawnee and Wichita. Between one-half and two-thirds of the Plains Indians had died of smallpox by the time of the Louisiana Purchase.[4]
European contact
With the arrival of Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, a Spanish conquistador, the first recorded history of encounter between Europeans and Native Americans in the Great Plains occurred in Texas, Kansas and Nebraska from 1540-1542. In that same time period, Hernando de Soto crossed a west-northwest direction in what is now Oklahoma and Texas. Today this is known as the De Soto Trail. The Spanish thought the Great Plains were the location of the mythological Quivira and Cíbola, a place said to be rich in gold.
Over the next one hundred years, founding of the fur trade brought thousands of ethnic Europeans into the Great Plains. Fur trappers from France, Spain, Britain, Russia and the young United States made their way across much of the region, making regular rendezvous with Native Americans and fur traders. After the United States acquired the Louisiana Purchase in 1803 and conducted the Lewis and Clark Expedition in 1804-1806, more information about the Plains became available and various pioneers entered the areas. Manuel Lisa, based in St. Louis, established a major fur trading site at his Fort Lisa on the Missouri River in Nebraska. Fur trading posts were often the basis of later settlements. Through the 19th century, more European Americans and Europeans migrated to the Great Plains as part of a vast westward expansion of population. New settlements became dotted across the Great Plains.
Early European settlements on the Great Plains
French
British


American
- Fort Manuel Lisa Trading Post (1806), Montana
- Fort Lisa (1809), North Dakota
- Fort Lisa (1812), Nebraska
- Fontenelle's Post (1822), Nebraska
- Cabanne's Trading Post (1822), Nebraska
Pioneer settlement
European-American settlement led to the near-extinction of the bison, especially after extension of the railroad across the Plains allowed hunters easy access to the herds. Sportshunters were most responsible for slaughtering the animals. Encroaching settlement by migrant farmers and ranchers led to increasing competition and conflict with Native Americans. In the end, settlers created so much political pressure that the United States removed the tribes to Indian reservations in the 1870s.
Much of the Great Plains became open range, hosting ranching operations where anyone was theoretically free to run cattle. In the spring and fall, ranchers held roundups where their cowboys branded new calves, treated animals and sorted the cattle for sale. Such ranching began in Texas and gradually moved northward. Cowboys drove Texas cattle north to railroad lines in the cities of Dodge City, Kansas and Ogallala, Nebraska; from there, cattle were shipped eastward. Many foreign, especially British, investors financed the great ranches of the era. Overstocking of the range and the terrible winter of 1886 resulted in a disaster, with many cattle starved and frozen to death. From then on, ranchers generally raised feed to ensure they could keep their cattle alive over winter.
To allow for agricultural development of the Great Plains and house a growing population, the US passed the Homestead Act of 1862: it allowed a settler to claim up to 160 acres (65 ha) of land, provided that he lived on it for a period of five years and cultivated it. The provisions were expanded under the Kinkaid Act to include a homestead of an entire section. Hundreds of thousands of people claimed such homesteads, sometimes building sod houses out of the very turf of their land. Many of them were not skilled dryland farmers and failures were frequent. Much of the Plains were settled during relatively wet years. Government experts did not understand how farmers should cultivate the prairies and gave advice counter to what would have worked. Germans from Russia who had previously farmed in familiar circumstances in what is now Ukraine were marginally more successful than the average homesteader. The Dominion Lands Act of 1871 served a similar function for establishing homesteads on the prairies in Canada.

After 1900
The region roughly centered on the Oklahoma Panhandle, including southeastern Colorado, southwestern Kansas, the Texas Panhandle, and extreme northeastern New Mexico was known as the Dust Bowl during the late 1920s and early 1930s. The effect of an extended drought, inappropriate cultivation, and financial crises of the Great Depression, forced many farmers off the land throughout the Great Plains.
From the 1950s on, many areas of the Great Plains have become productive crop-growing areas because of extensive irrigation on large landholdings. The southern portion of the Great Plains lies over the Ogallala Aquifer, a huge underground layer of water-bearing strata dating from the last ice age. Center pivot irrigation is used extensively in drier sections of the Great Plains, resulting in aquifer depletion at a rate that is greater than the ground's ability to recharge.
The rural Plains have lost a third of their population since 1920. Several hundred thousand square miles of the Great Plains have fewer than six persons per square mile—the density standard Frederick Jackson Turner used to declare the American frontier "closed" in 1893. Many have fewer than two persons per square mile.
There are more than 6,000 ghost towns in the state of Kansas alone, according to Kansas historian Daniel Fitzgerald. This problem is often exacerbated by the consolidation of farms and the difficulty of attracting modern industry to the region. In addition, the smaller school-age population has forced the consolidation of school districts and the closure of high schools in some communities. The continuing population loss among European Americans has led some to suggest that the current use of the drier parts of the Great Plains is not sustainable. One concept has been to propose restoration of large parts of the Plains to native grassland, accompanied by restocking of bison. This proposal is known as Buffalo Commons. Native American tribes are among those devoted to breeding and raising bison.


Wind power
The Great Plains contribute substantially to wind power in the United States. In July 2008, oilman turned wind-farm developer, T. Boone Pickens, called for the U.S. to invest $1 trillion to build an additional 200,000 MW of wind power nameplate capacity in the Plains, as part of his Pickens Plan. Pickens cited Sweetwater, Texas as an example of economic revitalization driven by wind power development.[6][7][8] Sweetwater was a struggling town typical of the Plains, steadily losing businesses and population, until wind turbines came to the surrounding Nolan County.[9] Wind power brought jobs to local residents, along with royalty payments to landowners who leased sites for turbines, reversing the town's population decline. Pickens claims the same economic benefits are possible throughout the Plains, which he refers to as North America's "wind corridor."
See also
|
|
References
Bibliography
- Paul Bonnifield, The Dust Bowl: Men, Dirt, and Depression, University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque, New Mexico, 1978, hardcover, ISBN 0-8263-0485-0.
- Timothy Eagan. The Worst Hard Time : the Untold Story of Those Who Survived the Great American Dust Bowl. Boston : Houghton Mifflin Co., 2006.
- Michael Forsberg, Great Plains: America's Lingering Wild, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, Illinois, 2009, ISBN 9780226257259
- D. H. Fairchild and J. E. Klete, Woody Landscape Plants for the High Plains, Colorado State University, 1993, Technical Bulletin LTB93-1 (Contact CSU to buy this).
- Merrill Gilfillan, Chokecherry Places, Essays from the High Plains, Johnson Press, Boulder, Colorado, trade paperback, ISBN 1-55566-227-7.
- Michael Johnston Grant, Down and Out on the Family Farm: Rural Rehabilitation in the Great Plains, 1929-1945, University of Nebraska Press, 2002, ISBN 0-8032-7105-0
- Harold Hamil, Colorado Without Mountains, A High Plains Memoir, The Lowell Press, Kansas City, Missouri, 1976, Hardback, 284 pages, ISBN 0-913504-33-5.
- Kent Haruf, The Tie That Binds (1984), a novel about farming by Vintage Books 2000, paperback, ISBN 0-375-72438-9.
- R. Douglas Hurt. The Great Plains during World War II. University of Nebraska Press. 2008. Pp. xiii, 507.
- Neal R. Peirce. The Great Plains States of America: People, Politics, and Power in the Nine Great Plains States (March 1973)
- Jonathan Raban. Bad Land: An American Romance. Vintage Departures, division of Vintage Books, New York, 1996. Winner of the National Book Critics Circle Award for Nonfiction.
- Wallace Stegner, Wolf Willow, A history, a story, and a memory of the last plains frontier, Viking Compass Book, New York, 1966, trade paperback, ISBN 0-670-00197-X
- David J. Wishart, ed. Encyclopedia of the Great Plains, University of Nebraska Press, 2004, ISBN 0-8032-4787-7.
- Answers.com
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wishart, David. 2004. The Great Plains Region, In: Encyclopedia of the Great Plains, Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, pp. xiii-xviii. ISBN 0-8032-4787-7
- ↑ "Ice Age Animals". Illinois State Museum.
- ↑ "A Plan For Reintroducing Megafauna To North America". ScienceDaily. October 2, 2006.
- ↑ "Emerging Infections: Microbial Threats to Health in the United States (1992)". Institute of Medicine (IOM).
- ↑ Rees, Amanda (2004). The Great Plains region. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 18. ISBN 0313327335. http://books.google.es/books?id=v0MpNai3xdMC. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- ↑ "Legendary Texas oilman embraces wind power". Star Tribune. 2008-07-25. http://www.startribune.com/business/25868279.html. Retrieved 2008-08-24.
- ↑ Fahey, Anna (2008-07-09). "Texas Oil Man Says We Can Break the Addiction". Sightline Daily. http://daily.sightline.org/daily_score/archive/200Accept-Encoding:gzip,deflateAn-break-the-addiction. Retrieved 2008-08-24.
- ↑ "T. Boone Pickens Places $2 Billion Order for GE Wind Turbines". Wind Today Magazine. 2008-05-16. http://www.windtoday.net/info/articles.html?ID=57318. Retrieved 2008-08-24.
- ↑ Block, Ben (2008-07-24). "In Windy West Texas, An Economic Boom". http://www.worldchanging.com/archives/008271.html. Retrieved 2008-11-05.
External links
- Kansas Heritage Group: Native Prairie, Preseve, Flowers, and Research
- Library of Congress: Great Plains
- University of Nebraska-Lincoln: The Great Plains Study
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
